ICTC 3104.3 Data Analytics and Big Data
Data Import and Data Wrangling with R
2020-08-20
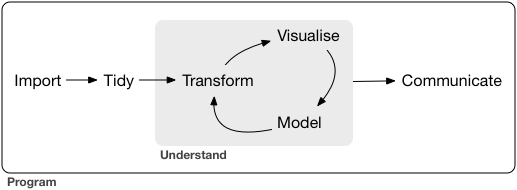
Outline
Basics of R Programming ✅
Data Import ⚙️
Data Wrangling
Data Visualization
Data Import
Setup
install.packages("tidyverse") # install tidyverse packageslibrary(tidyverse) # load tidyverse packages

Tibble
Tibbles are data frames.
A modern re-imagining of data frames.
Create a tibble
library(tidyverse) # library(tibble)first.tbl <- tibble(height = c(150, 200, 160), weight = c(45, 60, 51))first.tbl# A tibble: 3 x 2 height weight <dbl> <dbl>1 150 452 200 603 160 51class(first.tbl)[1] "tbl_df" "tbl" "data.frame"tibble vs. data.frame
- Output
tibble
first.tbl <- tibble(height = c(150, 200, 160), weight = c(45, 60, 51))first.tbl# A tibble: 3 x 2 height weight <dbl> <dbl>1 150 452 200 603 160 51data.frame
dataframe <- data.frame(height = c(150, 200, 160), weight = c(45, 60, 51))dataframe height weight1 150 452 200 603 160 51tibble vs. data.frame (cont.)
- You can create new variables that are functions of existing variables.
tibble
first.tbl <- tibble(height = c(150, 200, 160), weight = c(45, 60, 51), bmi = (weight)/height^2)first.tbl# A tibble: 3 x 3 height weight bmi <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>1 150 45 0.002 2 200 60 0.0015 3 160 51 0.00199data.frame
df <- data.frame(height = c(150, 200, 160), weight = c(45, 60, 51), bmi = (weight)/height^2) # Not workingYou will get an error message
Error in data.frame(height = c(150, 200, 160), weight = c(45, 60, 51), :
object 'height' not found.
Pipe operator: %>%
Required package: magrittr
install.packages("magrittr")library(magrittr)What does it do?
It takes whatever is on the left-hand-side of the pipe and makes it the first argument of whatever function is on the right-hand-side of the pipe.
For instance,
mean(1:10)[1] 5.5can be written as
1:10 %>% mean()[1] 5.5🛠 Import data from a .csv file
datasetname <- read_csv("include_file_path")When you run read_csv, it prints out the names and type of each column.
Demo: Switch to R
🛠 Importing csv file from a website
Syntax
datasetname <- read_csv("include url here")Example
url <- "https://thiyanga.netlify.app/project/datasets/foodlabel.csv"foodlabel <- read_csv(url)head(foodlabel, 1)🛠 Writing to a File
We can save tibble (or dataframe) to a csv file, using
write_csv().write_csv()is in thereadrpackage.
Syntax
write_csv(name_of_the_data_set_you_want_to_save, "path_to_write_to")Example
data(gapminder)# This will save inside your project folderwrite_csv(gaominder, "gapminder.csv") # This will save inside the data folder which is inside your project folderwrite_csv(gapminder, "data/gapminder.csv")Demo: Switch to R
🛠 Importing Excel .xlsx files
Syntax
library(readxl)mydata <- read_xlsx("file_path")Demo: Switch to R
Outline
Basics of R Programming ✅
Data Import ✅
Data Wrangling ⚙️
Data Visualization
Data Wrangling

Data Wrangling/ Data Munging
Data Wrangling/ Data Munging

Reshaping Data (tidying your data)
How to reshape your data in order to make the analysis easier.
Tidy Data

Each variable is saved in its column.
Each observation is saved in its own row.
Image Credit: Hadley Wickham and Garrett Grolemund
packages
library(tidyverse) #or library(tidyr)library(magrittr)library(gapminder)

tidyr package
Hadley Wickham (Chief Scientist at RStudio) is explaining tidyr at WOMBAT organized by Monash University, Australia.
Image rights: Thiyanga S Talagala
tidyr verbs
Main verbs
pivot_longerIn tidyr (2014)
gatherpivot_widerIn tidyr (2014)
spread
Other
separateunite
Input and Output
Main input: data frame or tibble.
Output: tibble
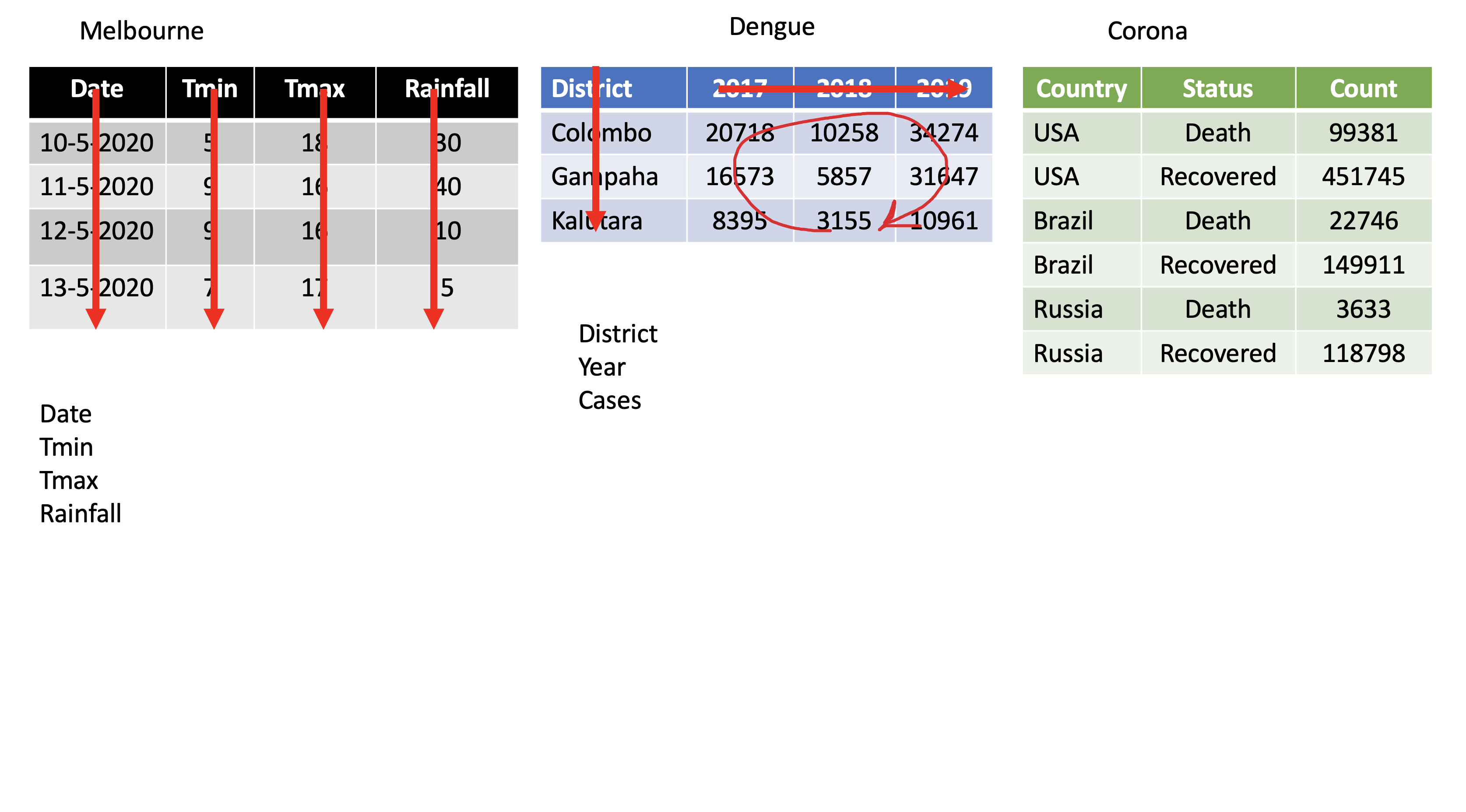
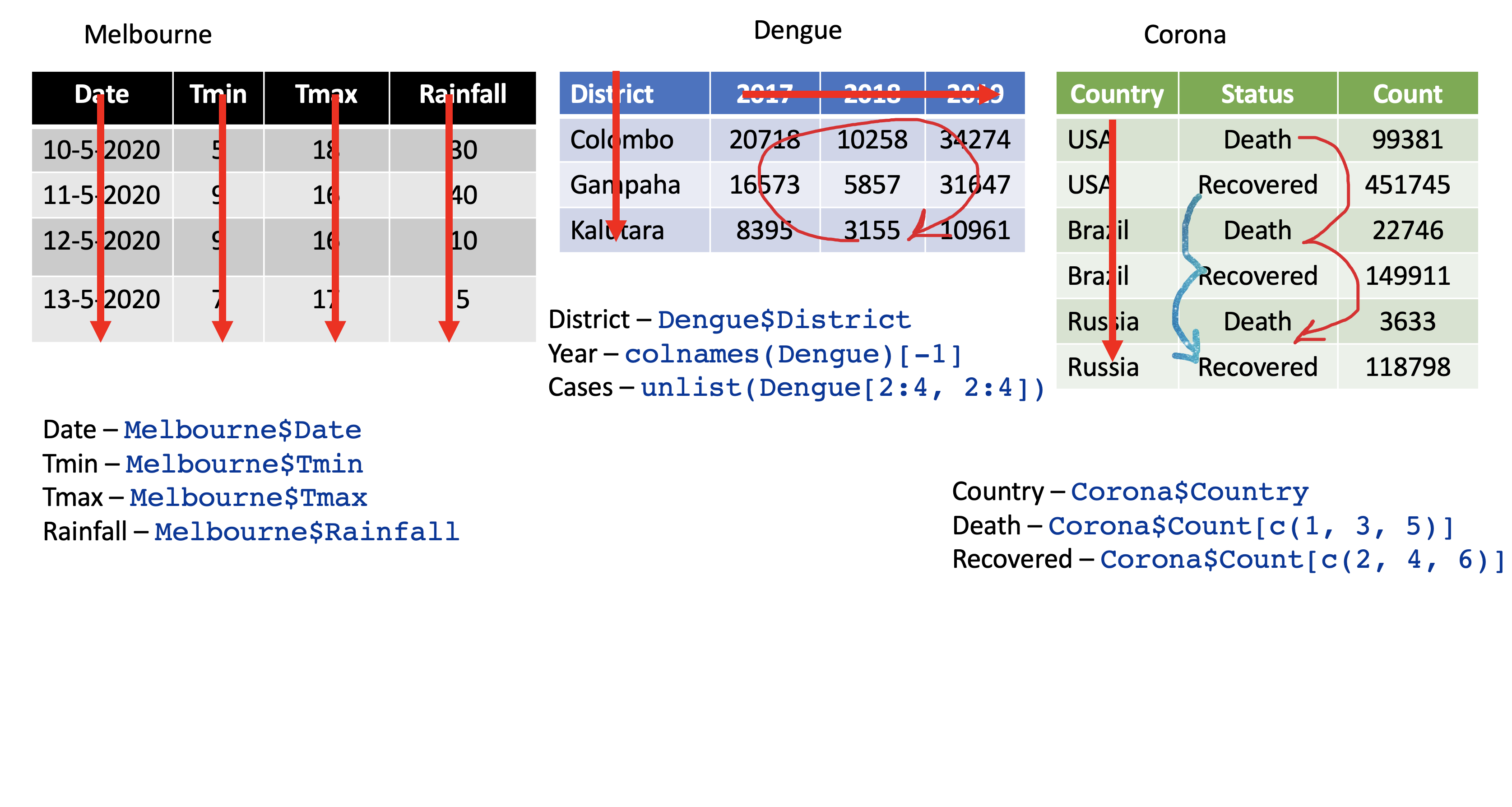
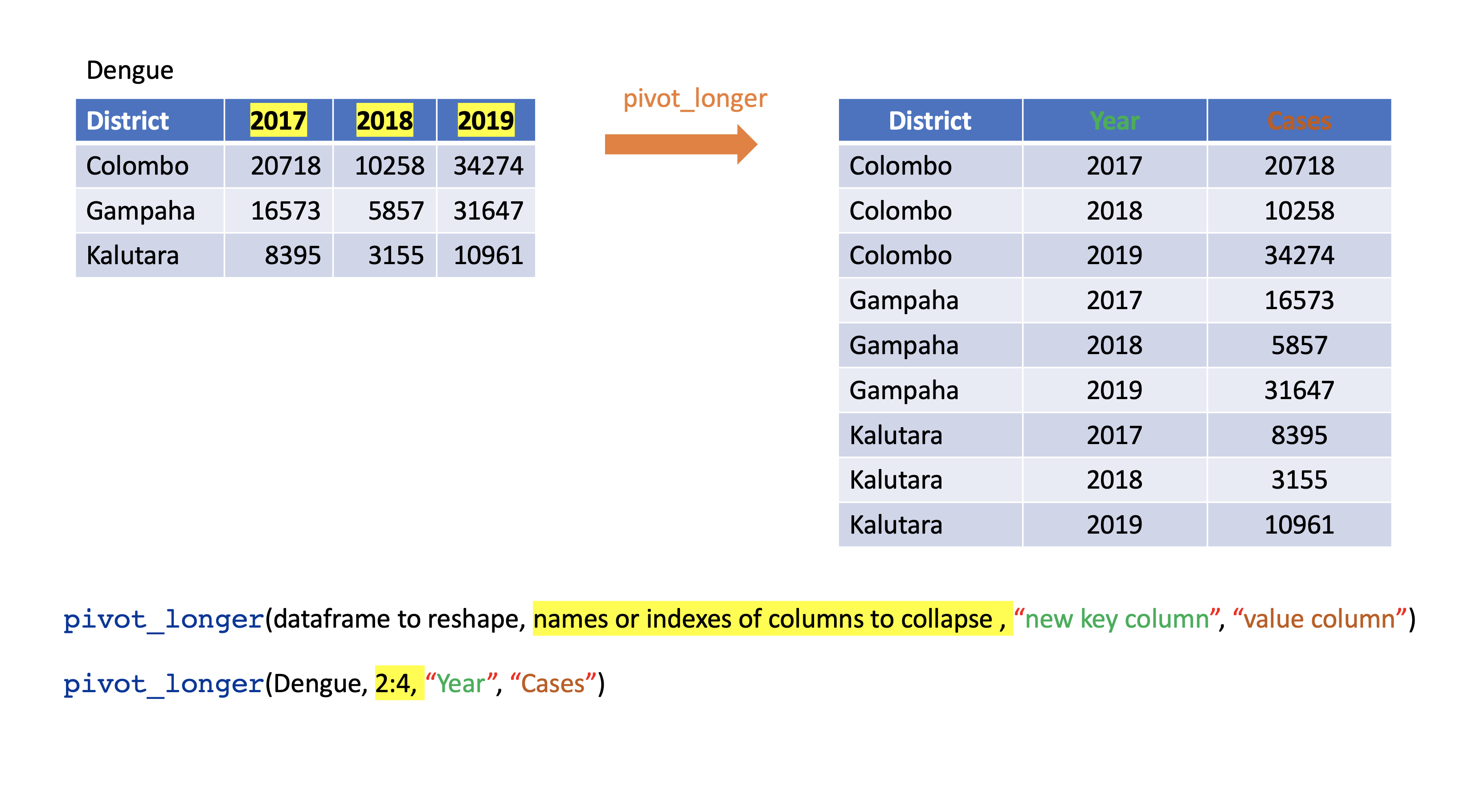
pivot_longer
pivot_longer()
Turns columns into rows.
From wide format to long format.
pivot_longer()
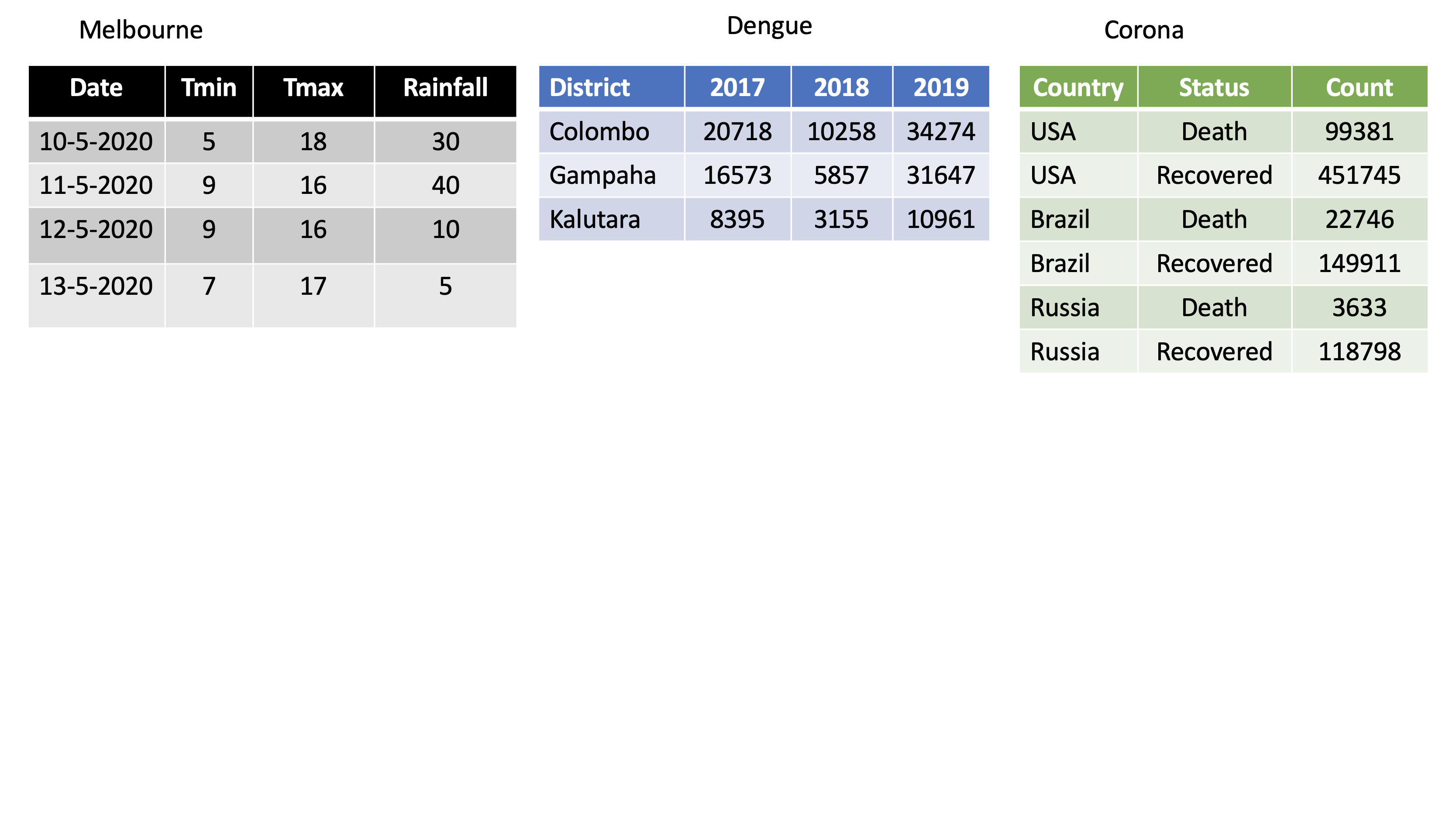
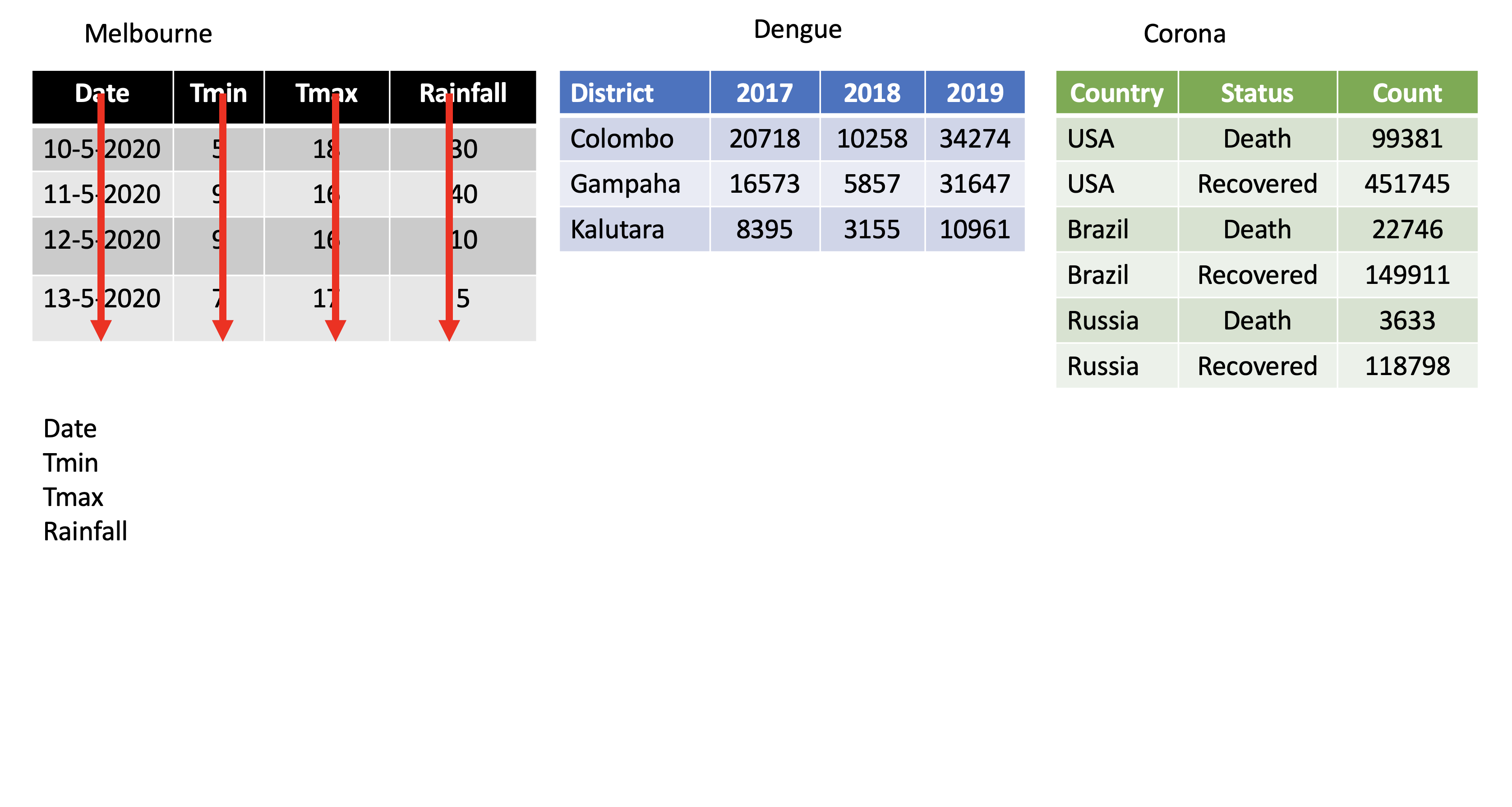
dengue <- tibble( dist = c("Colombo", "Gampaha", "Kalutara"), '2017' = c(20718, 10258, 34274), '2018' = c(16573, 5857, 31647), '2019' = c(8395, 3155, 10961)); dengue# A tibble: 3 x 4 dist `2017` `2018` `2019` <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>1 Colombo 20718 16573 83952 Gampaha 10258 5857 31553 Kalutara 34274 31647 10961dengue %>% pivot_longer(2:4, names_to="Year", values_to = "Dengue counts")# A tibble: 9 x 3 dist Year `Dengue counts` <chr> <chr> <dbl>1 Colombo 2017 207182 Colombo 2018 165733 Colombo 2019 83954 Gampaha 2017 102585 Gampaha 2018 58576 Gampaha 2019 31557 Kalutara 2017 342748 Kalutara 2018 316479 Kalutara 2019 10961pivot_wider
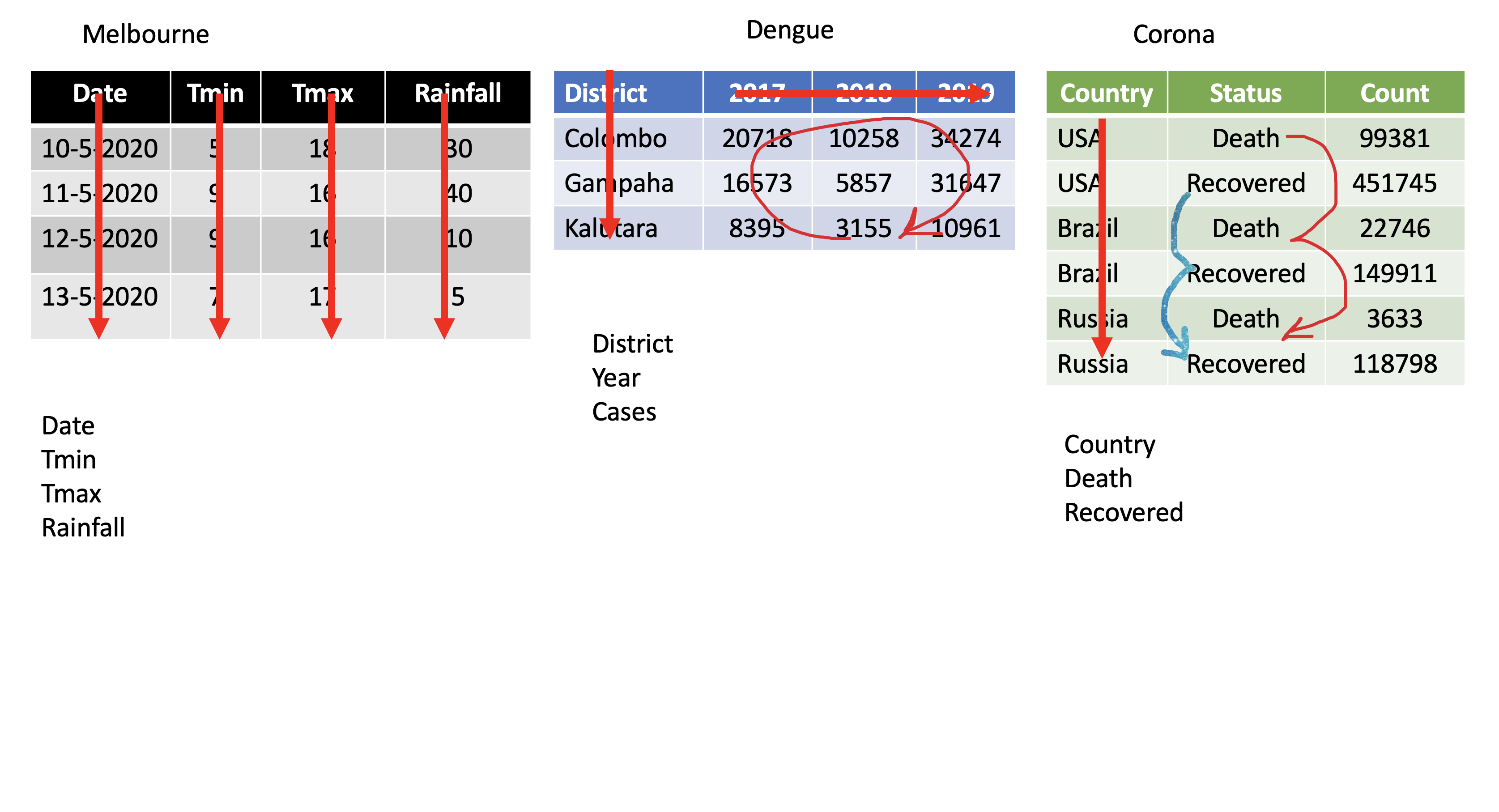
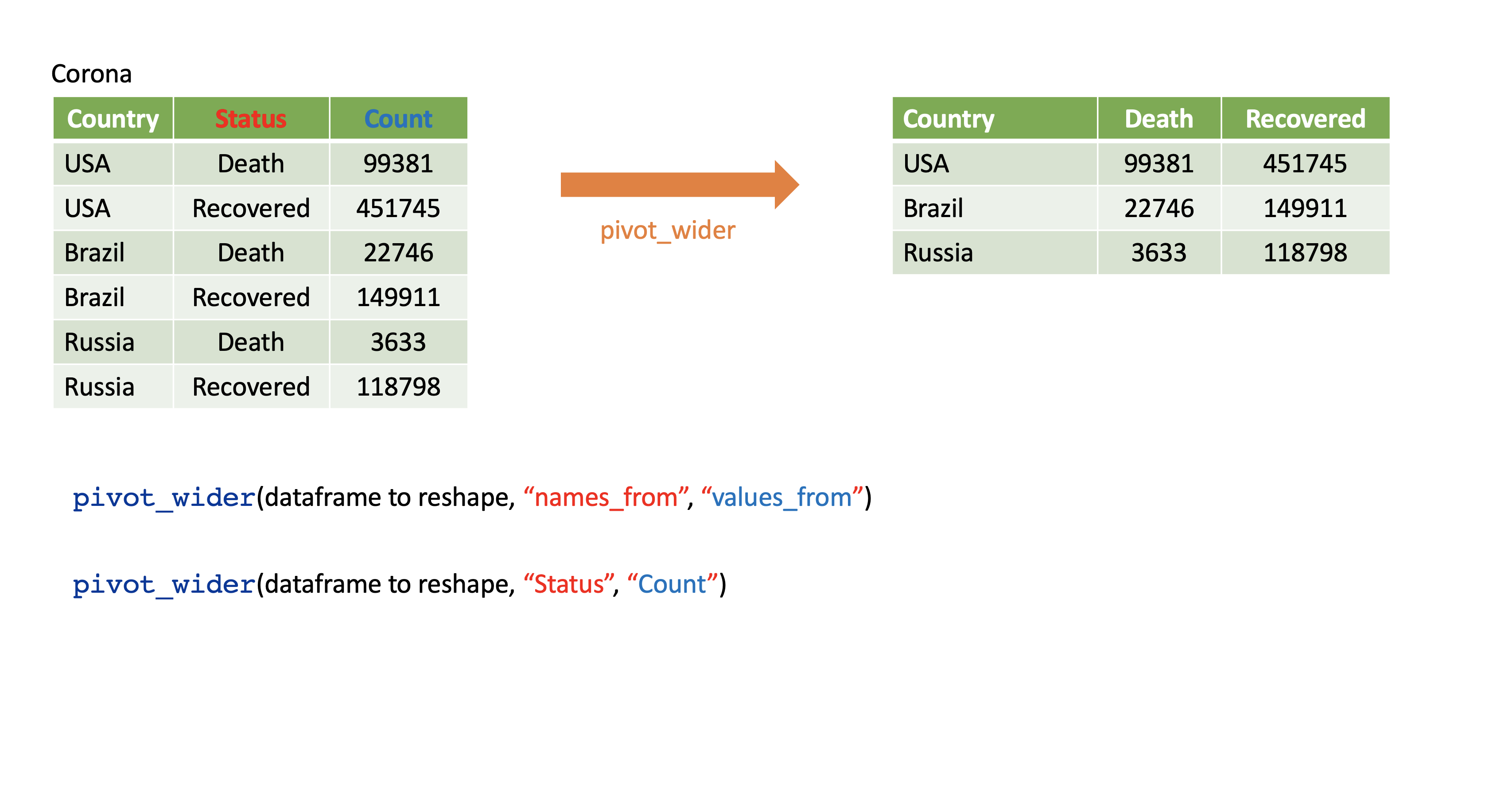
pivot_wider()
- From long to wide format.
pivot_wider()
Corona <- tibble(country = rep(c("USA", "Brazil", "Russia"), each=2),status = rep(c("Death", "Recovered"), 3),count = c(99381, 451745, 22746, 149911, 3633, 118798))Corona# A tibble: 6 x 3 country status count <chr> <chr> <dbl>1 USA Death 993812 USA Recovered 4517453 Brazil Death 227464 Brazil Recovered 1499115 Russia Death 36336 Russia Recovered 118798pivot_wider()
Corona# A tibble: 6 x 3 country status count <chr> <chr> <dbl>1 USA Death 993812 USA Recovered 4517453 Brazil Death 227464 Brazil Recovered 1499115 Russia Death 36336 Russia Recovered 118798Corona %>% pivot_wider(names_from=status, values_from=count)# A tibble: 3 x 3 country Death Recovered <chr> <dbl> <dbl>1 USA 99381 4517452 Brazil 22746 1499113 Russia 3633 118798Assign a name:
corona_wide_format <- Corona %>% pivot_wider(names_from=status, values_from=count)corona_wide_format# A tibble: 3 x 3 country Death Recovered <chr> <dbl> <dbl>1 USA 99381 4517452 Brazil 22746 1499113 Russia 3633 118798pivot_longer vs pivot_wider
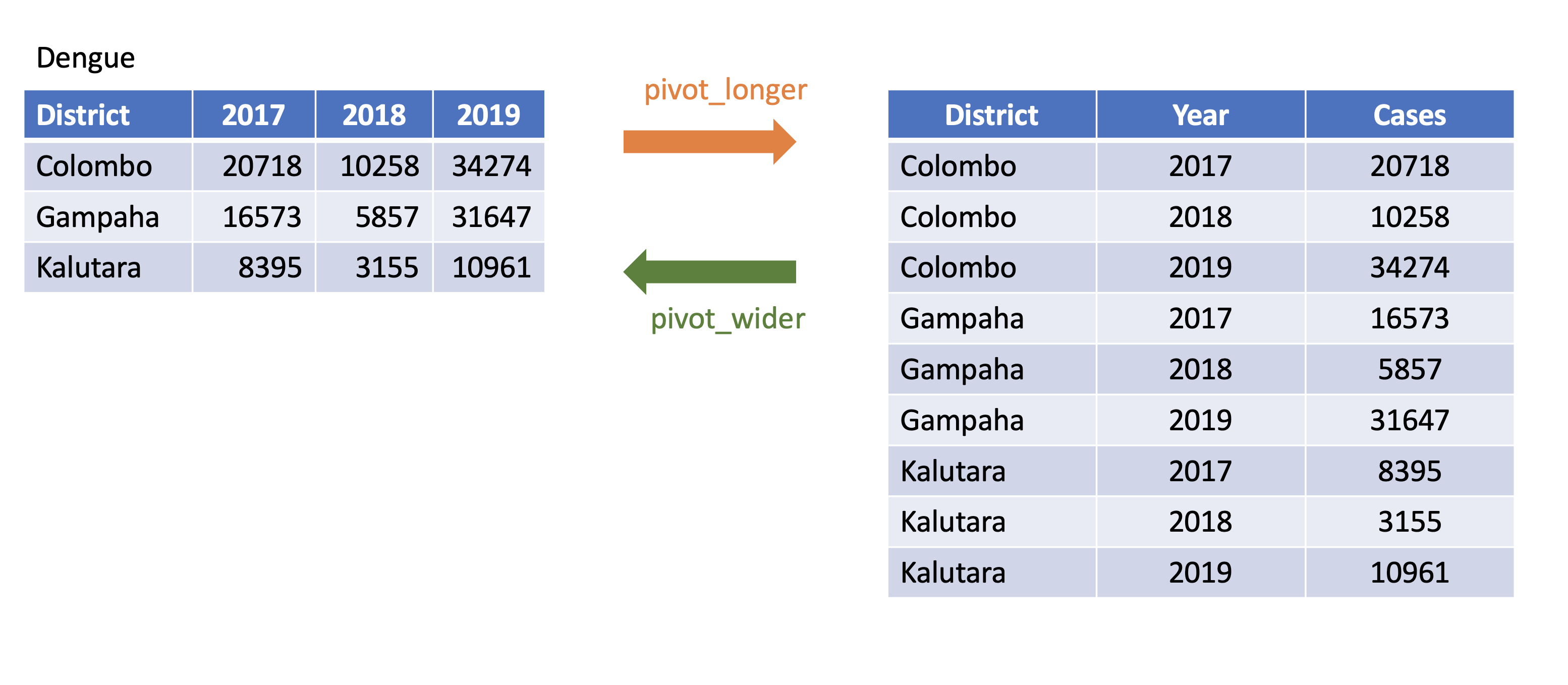
pivot_longer and pivot_wider
profit <- tibble(year = c(2015, 2015, 2015, 2015, 2016, 2016, 2016),quarter = c( 1, 2, 3, 4, 2, 3, 4),income = c(2, NA, 3, NA, 4, 5, 6))profit# A tibble: 7 x 3 year quarter income <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>1 2015 1 22 2015 2 NA3 2015 3 34 2015 4 NA5 2016 2 46 2016 3 57 2016 4 6pivot_longer and pivot_wider
# A tibble: 7 x 3 year quarter income <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>1 2015 1 22 2015 2 NA3 2015 3 34 2015 4 NA5 2016 2 46 2016 3 57 2016 4 6profit %>%pivot_wider(names_from = year, values_from = income)# A tibble: 4 x 3 quarter `2015` `2016` <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>1 1 2 NA2 2 NA 43 3 3 54 4 NA 6Missing values
# A tibble: 4 x 3 quarter `2015` `2016` <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>1 1 2 NA2 2 NA 43 3 3 54 4 NA 6profit %>%pivot_wider(names_from = year, values_from = income) %>%pivot_longer(cols = c(`2015`, `2016`),names_to = "year",values_to = "income",values_drop_na = TRUE)# A tibble: 5 x 3 quarter year income <dbl> <chr> <dbl>1 1 2015 22 2 2016 43 3 2015 34 3 2016 55 4 2016 6dplyr verbs
filterselectmutatesummarisearrangegroup_byrename
filter
Picks observations by their values.
Takes logical expressions and returns the rows for which all are
TRUE.
filter(gapminder, lifeExp < 50)# A tibble: 491 x 6 country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap <fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl> 1 Afghanistan Asia 1952 28.8 8425333 779. 2 Afghanistan Asia 1957 30.3 9240934 821. 3 Afghanistan Asia 1962 32.0 10267083 853. 4 Afghanistan Asia 1967 34.0 11537966 836. 5 Afghanistan Asia 1972 36.1 13079460 740. 6 Afghanistan Asia 1977 38.4 14880372 786. 7 Afghanistan Asia 1982 39.9 12881816 978. 8 Afghanistan Asia 1987 40.8 13867957 852. 9 Afghanistan Asia 1992 41.7 16317921 649.10 Afghanistan Asia 1997 41.8 22227415 635.# … with 481 more rowsfilter (cont)
filter(gapminder, country == "Sri Lanka")# A tibble: 12 x 6 country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap <fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl> 1 Sri Lanka Asia 1952 57.6 7982342 1084. 2 Sri Lanka Asia 1957 61.5 9128546 1073. 3 Sri Lanka Asia 1962 62.2 10421936 1074. 4 Sri Lanka Asia 1967 64.3 11737396 1136. 5 Sri Lanka Asia 1972 65.0 13016733 1213. 6 Sri Lanka Asia 1977 65.9 14116836 1349. 7 Sri Lanka Asia 1982 68.8 15410151 1648. 8 Sri Lanka Asia 1987 69.0 16495304 1877. 9 Sri Lanka Asia 1992 70.4 17587060 2154.10 Sri Lanka Asia 1997 70.5 18698655 2664.11 Sri Lanka Asia 2002 70.8 19576783 3015.12 Sri Lanka Asia 2007 72.4 20378239 3970.# gapminder %>% filter(country == "Sri Lanka")filter (cont)
filter(gapminder, country %in% c("Sri Lanka", "Australia"))# A tibble: 24 x 6 country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap <fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl> 1 Australia Oceania 1952 69.1 8691212 10040. 2 Australia Oceania 1957 70.3 9712569 10950. 3 Australia Oceania 1962 70.9 10794968 12217. 4 Australia Oceania 1967 71.1 11872264 14526. 5 Australia Oceania 1972 71.9 13177000 16789. 6 Australia Oceania 1977 73.5 14074100 18334. 7 Australia Oceania 1982 74.7 15184200 19477. 8 Australia Oceania 1987 76.3 16257249 21889. 9 Australia Oceania 1992 77.6 17481977 23425.10 Australia Oceania 1997 78.8 18565243 26998.# … with 14 more rowsfilter (cont)
filter(gapminder, country %in% c("Sri Lanka", "Australia")) %>% head()# A tibble: 6 x 6 country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap <fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl>1 Australia Oceania 1952 69.1 8691212 10040.2 Australia Oceania 1957 70.3 9712569 10950.3 Australia Oceania 1962 70.9 10794968 12217.4 Australia Oceania 1967 71.1 11872264 14526.5 Australia Oceania 1972 71.9 13177000 16789.6 Australia Oceania 1977 73.5 14074100 18334.filter(gapminder, country %in% c("Sri Lanka", "Australia")) %>% tail()# A tibble: 6 x 6 country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap <fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl>1 Sri Lanka Asia 1982 68.8 15410151 1648.2 Sri Lanka Asia 1987 69.0 16495304 1877.3 Sri Lanka Asia 1992 70.4 17587060 2154.4 Sri Lanka Asia 1997 70.5 18698655 2664.5 Sri Lanka Asia 2002 70.8 19576783 3015.6 Sri Lanka Asia 2007 72.4 20378239 3970.select
- Picks variables by their names.
head(gapminder, 3)# A tibble: 3 x 6 country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap <fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl>1 Afghanistan Asia 1952 28.8 8425333 779.2 Afghanistan Asia 1957 30.3 9240934 821.3 Afghanistan Asia 1962 32.0 10267083 853.select(gapminder, year:gdpPercap)# A tibble: 1,704 x 4 year lifeExp pop gdpPercap <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl> 1 1952 28.8 8425333 779. 2 1957 30.3 9240934 821. 3 1962 32.0 10267083 853. 4 1967 34.0 11537966 836. 5 1972 36.1 13079460 740. 6 1977 38.4 14880372 786. 7 1982 39.9 12881816 978. 8 1987 40.8 13867957 852. 9 1992 41.7 16317921 649.10 1997 41.8 22227415 635.# … with 1,694 more rowsselect (cont.)
head(gapminder, 3)# A tibble: 3 x 6 country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap <fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl>1 Afghanistan Asia 1952 28.8 8425333 779.2 Afghanistan Asia 1957 30.3 9240934 821.3 Afghanistan Asia 1962 32.0 10267083 853.select(gapminder, year, gdpPercap)# A tibble: 1,704 x 2 year gdpPercap <int> <dbl> 1 1952 779. 2 1957 821. 3 1962 853. 4 1967 836. 5 1972 740. 6 1977 786. 7 1982 978. 8 1987 852. 9 1992 649.10 1997 635.# … with 1,694 more rowsselect (cont.)
head(gapminder, 3)# A tibble: 3 x 6 country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap <fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl>1 Afghanistan Asia 1952 28.8 8425333 779.2 Afghanistan Asia 1957 30.3 9240934 821.3 Afghanistan Asia 1962 32.0 10267083 853.select(gapminder, -c(year, gdpPercap))# A tibble: 1,704 x 4 country continent lifeExp pop <fct> <fct> <dbl> <int> 1 Afghanistan Asia 28.8 8425333 2 Afghanistan Asia 30.3 9240934 3 Afghanistan Asia 32.0 10267083 4 Afghanistan Asia 34.0 11537966 5 Afghanistan Asia 36.1 13079460 6 Afghanistan Asia 38.4 14880372 7 Afghanistan Asia 39.9 12881816 8 Afghanistan Asia 40.8 13867957 9 Afghanistan Asia 41.7 1631792110 Afghanistan Asia 41.8 22227415# … with 1,694 more rowsselect (cont.)
head(gapminder, 3)# A tibble: 3 x 6 country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap <fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl>1 Afghanistan Asia 1952 28.8 8425333 779.2 Afghanistan Asia 1957 30.3 9240934 821.3 Afghanistan Asia 1962 32.0 10267083 853.select(gapminder, -(year:gdpPercap))# A tibble: 1,704 x 2 country continent <fct> <fct> 1 Afghanistan Asia 2 Afghanistan Asia 3 Afghanistan Asia 4 Afghanistan Asia 5 Afghanistan Asia 6 Afghanistan Asia 7 Afghanistan Asia 8 Afghanistan Asia 9 Afghanistan Asia 10 Afghanistan Asia # … with 1,694 more rowsmutate
- Creates new variables with functions of existing variables
gapminder %>%mutate(gdp = pop * gdpPercap)# A tibble: 1,704 x 7 country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap gdp <fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <dbl> 1 Afghanistan Asia 1952 28.8 8425333 779. 6567086330. 2 Afghanistan Asia 1957 30.3 9240934 821. 7585448670. 3 Afghanistan Asia 1962 32.0 10267083 853. 8758855797. 4 Afghanistan Asia 1967 34.0 11537966 836. 9648014150. 5 Afghanistan Asia 1972 36.1 13079460 740. 9678553274. 6 Afghanistan Asia 1977 38.4 14880372 786. 11697659231. 7 Afghanistan Asia 1982 39.9 12881816 978. 12598563401. 8 Afghanistan Asia 1987 40.8 13867957 852. 11820990309. 9 Afghanistan Asia 1992 41.7 16317921 649. 10595901589.10 Afghanistan Asia 1997 41.8 22227415 635. 14121995875.# … with 1,694 more rowssummarise(British) or summarize (US)
- Collapse many values down to a single summary
gapminder %>% summarise( lifeExp_mean=mean(lifeExp), pop_mean=mean(pop), gdpPercap_mean=mean(gdpPercap))# A tibble: 1 x 3 lifeExp_mean pop_mean gdpPercap_mean <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>1 59.5 29601212. 7215.arrange
- Reorder the rows
arrange(gapminder, desc(lifeExp))# A tibble: 1,704 x 6 country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap <fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl> 1 Japan Asia 2007 82.6 127467972 31656. 2 Hong Kong, China Asia 2007 82.2 6980412 39725. 3 Japan Asia 2002 82 127065841 28605. 4 Iceland Europe 2007 81.8 301931 36181. 5 Switzerland Europe 2007 81.7 7554661 37506. 6 Hong Kong, China Asia 2002 81.5 6762476 30209. 7 Australia Oceania 2007 81.2 20434176 34435. 8 Spain Europe 2007 80.9 40448191 28821. 9 Sweden Europe 2007 80.9 9031088 33860.10 Israel Asia 2007 80.7 6426679 25523.# … with 1,694 more rowsgroup_by
- Takes an existing tibble and converts it into a grouped tibble where operations are performed "by group". ungroup() removes grouping.
Japan_SL <- filter(gapminder, country %in% c("Japan", "Sri Lanka"))Japan_SL %>% head()# A tibble: 6 x 6 country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap <fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl>1 Japan Asia 1952 63.0 86459025 3217.2 Japan Asia 1957 65.5 91563009 4318.3 Japan Asia 1962 68.7 95831757 6577.4 Japan Asia 1967 71.4 100825279 9848.5 Japan Asia 1972 73.4 107188273 14779.6 Japan Asia 1977 75.4 113872473 16610.Japan_SL_grouped <- Japan_SL %>% group_by(country)Japan_SL_grouped# A tibble: 24 x 6# Groups: country [2] country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap <fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl> 1 Japan Asia 1952 63.0 86459025 3217. 2 Japan Asia 1957 65.5 91563009 4318. 3 Japan Asia 1962 68.7 95831757 6577. 4 Japan Asia 1967 71.4 100825279 9848. 5 Japan Asia 1972 73.4 107188273 14779. 6 Japan Asia 1977 75.4 113872473 16610. 7 Japan Asia 1982 77.1 118454974 19384. 8 Japan Asia 1987 78.7 122091325 22376. 9 Japan Asia 1992 79.4 124329269 26825.10 Japan Asia 1997 80.7 125956499 28817.# … with 14 more rowsgroup_by (cont.)
Japan_SL %>% summarise(mean_lifeExp=mean(lifeExp))# A tibble: 1 x 1 mean_lifeExp <dbl>1 70.7Japan_SL_grouped %>% summarise(mean_lifeExp=mean(lifeExp))# A tibble: 2 x 2 country mean_lifeExp <fct> <dbl>1 Japan 74.82 Sri Lanka 66.5rename
- Rename variables
head(gapminder, 3)# A tibble: 3 x 6 country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap <fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl>1 Afghanistan Asia 1952 28.8 8425333 779.2 Afghanistan Asia 1957 30.3 9240934 821.3 Afghanistan Asia 1962 32.0 10267083 853.rename(gapminder, `life expectancy`=lifeExp, population=pop) # new_name = old_name# A tibble: 1,704 x 6 country continent year `life expectancy` population gdpPercap <fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl> 1 Afghanistan Asia 1952 28.8 8425333 779. 2 Afghanistan Asia 1957 30.3 9240934 821. 3 Afghanistan Asia 1962 32.0 10267083 853. 4 Afghanistan Asia 1967 34.0 11537966 836. 5 Afghanistan Asia 1972 36.1 13079460 740. 6 Afghanistan Asia 1977 38.4 14880372 786. 7 Afghanistan Asia 1982 39.9 12881816 978. 8 Afghanistan Asia 1987 40.8 13867957 852. 9 Afghanistan Asia 1992 41.7 16317921 649.10 Afghanistan Asia 1997 41.8 22227415 635.# … with 1,694 more rowsCombine multiple operations
gapminder %>%filter(country == 'China') %>% head(2)# A tibble: 2 x 6 country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap <fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl>1 China Asia 1952 44 556263527 400.2 China Asia 1957 50.5 637408000 576.gapminder %>%filter(country == 'China') %>% summarise(lifemax=max(lifeExp))# A tibble: 1 x 1 lifemax <dbl>1 73.0gapminder %>%filter(country == 'China') %>%filter(lifeExp == max(lifeExp))# A tibble: 1 x 6 country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap <fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl>1 China Asia 2007 73.0 1318683096 4959.Combine multiple operations
gapminder %>%filter(continent == 'Asia') %>%group_by(country) %>%filter(lifeExp == max(lifeExp)) %>%arrange(desc(year))# A tibble: 33 x 6# Groups: country [33] country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap <fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl> 1 Afghanistan Asia 2007 43.8 31889923 975. 2 Bahrain Asia 2007 75.6 708573 29796. 3 Bangladesh Asia 2007 64.1 150448339 1391. 4 Cambodia Asia 2007 59.7 14131858 1714. 5 China Asia 2007 73.0 1318683096 4959. 6 Hong Kong, China Asia 2007 82.2 6980412 39725. 7 India Asia 2007 64.7 1110396331 2452. 8 Indonesia Asia 2007 70.6 223547000 3541. 9 Iran Asia 2007 71.0 69453570 11606.10 Israel Asia 2007 80.7 6426679 25523.# … with 23 more rowsCombine Data Sets
Combine Data Sets
Mutating joins
left_joinright_joininner_joinfull_join
Set operations
intersectunion
Binding
bind_rowsbind_cols
left_join
first <- tibble(x1=c("A", "B", "C"), x2=c(1, 2, 3))second <- tibble(x1=c("A", "B", "D"), x3=c("red", "yellow" , "green"))first# A tibble: 3 x 2 x1 x2 <chr> <dbl>1 A 12 B 23 C 3second# A tibble: 3 x 2 x1 x3 <chr> <chr> 1 A red 2 B yellow3 D greenleft_join(first, second, by="x1")# A tibble: 3 x 3 x1 x2 x3 <chr> <dbl> <chr> 1 A 1 red 2 B 2 yellow3 C 3 <NA>right_join
first <- tibble(x1=c("A", "B", "C"), x2=c(1, 2, 3))second <- tibble(x1=c("A", "B", "D"), x3=c("red", "yellow" , "green"))first# A tibble: 3 x 2 x1 x2 <chr> <dbl>1 A 12 B 23 C 3second# A tibble: 3 x 2 x1 x3 <chr> <chr> 1 A red 2 B yellow3 D greenright_join(first, second, by="x1")# A tibble: 3 x 3 x1 x2 x3 <chr> <dbl> <chr> 1 A 1 red 2 B 2 yellow3 D NA greeninner_join
first <- tibble(x1=c("A", "B", "C"), x2=c(1, 2, 3))second <- tibble(x1=c("A", "B", "D"), x3=c("red", "yellow" , "green"))first# A tibble: 3 x 2 x1 x2 <chr> <dbl>1 A 12 B 23 C 3second# A tibble: 3 x 2 x1 x3 <chr> <chr> 1 A red 2 B yellow3 D greeninner_join(first, second, by="x1")# A tibble: 2 x 3 x1 x2 x3 <chr> <dbl> <chr> 1 A 1 red 2 B 2 yellowfull_join
first <- tibble(x1=c("A", "B", "C"), x2=c(1, 2, 3))second <- tibble(x1=c("A", "B", "D"), x3=c("red", "yellow" , "green"))first# A tibble: 3 x 2 x1 x2 <chr> <dbl>1 A 12 B 23 C 3second# A tibble: 3 x 2 x1 x3 <chr> <chr> 1 A red 2 B yellow3 D greenfull_join(first, second, by="x1")# A tibble: 4 x 3 x1 x2 x3 <chr> <dbl> <chr> 1 A 1 red 2 B 2 yellow3 C 3 <NA> 4 D NA greenSet operations
first <- tibble(x1=c("A", "B", "C"), x2=c(1, 2, 3))second <- tibble(x1=c("D", "B", "C"), x2=c(10, 2, 3))Two compatible data sets. Column names are the same.
first# A tibble: 3 x 2 x1 x2 <chr> <dbl>1 A 12 B 23 C 3second# A tibble: 3 x 2 x1 x2 <chr> <dbl>1 D 102 B 23 C 3intersect
intersect(first, second)# A tibble: 2 x 2 x1 x2 <chr> <dbl>1 B 22 C 3union
union(first, second)# A tibble: 4 x 2 x1 x2 <chr> <dbl>1 A 12 B 23 C 34 D 10Set operations (cont.)
first <- tibble(x1=c("A", "B", "C"), x2=c(1, 2, 3))second <- tibble(x1=c("D", "B", "C"), x2=c(10, 20, 30))Two compatible data sets. Column names are the same.
first# A tibble: 3 x 2 x1 x2 <chr> <dbl>1 A 12 B 23 C 3second# A tibble: 3 x 2 x1 x2 <chr> <dbl>1 D 102 B 203 C 30intersect
intersect(first, second)# A tibble: 0 x 2# … with 2 variables: x1 <chr>, x2 <dbl>union
union(first, second)# A tibble: 6 x 2 x1 x2 <chr> <dbl>1 A 12 B 23 C 34 D 105 B 206 C 30Binding
first <- tibble(x1=c("A", "B", "C"), x2=c(1, 2, 3))second <- tibble(x1=c("D", "B", "C"), x2=c(10, 20, 30))first# A tibble: 3 x 2 x1 x2 <chr> <dbl>1 A 12 B 23 C 3second# A tibble: 3 x 2 x1 x2 <chr> <dbl>1 D 102 B 203 C 30bind_rows
bind_rows(first, second)# A tibble: 6 x 2 x1 x2 <chr> <dbl>1 A 12 B 23 C 34 D 105 B 206 C 30Binding (cont.)
first <- tibble(x1=c("A", "B", "C"), x2=c(1, 2, 3))second <- tibble(x1=c("D", "B", "C"), x2=c(10, 20, 30))first# A tibble: 3 x 2 x1 x2 <chr> <dbl>1 A 12 B 23 C 3second# A tibble: 3 x 2 x1 x2 <chr> <dbl>1 D 102 B 203 C 30bind_cols
bind_cols(first, second)# A tibble: 3 x 4 x1...1 x2...2 x1...3 x2...4 <chr> <dbl> <chr> <dbl>1 A 1 D 102 B 2 B 203 C 3 C 30